The leather export business: everything you need to know
Blog Credits: https://www.fiverr.com/ajeetsingh430
BRIEF INTRODUCTION OF THIS ARTICLE
- How can you source the most sustainable leather and leather product for your export businesses?
- Future of leather industry in India
- Total export of leather from all over the country
- Total export of leather from Kanpur
- Why is leather mostly exported from India?
- India's leather export data for various countries
- India's leather export data w.r.t. goods
- Structure of the leather industry
- Leather industry in the global market
- What is the process of leather production - step by step
- Different types of leather are explained in detailed
- Important abbreviations for different types of leather
- Recognizing leather types: tips
- Important tips before sourcing leather as well as leather products for export
- List of leather products
- How to start your leather business - step by step

1. How can you source the most sustainable leather and leather product for your export businesses?
India is one of the world's largest exporters of leather and leather products. Although India's leather industry is spread across many cities, it is predominantly concentrated in mainly three cities:
- Kanpur (the Leather City of the World, Manchester of the East)
- Chennai
- Kolkata
Kanpur is the largest buffalo leather-producing city, while Chennai is home to the biggest goat leather industry and Kolkata is home to the biggest cow leather industry.
- There is no doubt that Indian leather is highly regarded throughout the world for its fine grain pattern, uniform fiber structure, and smooth texture.
- More than 85% of Indian leather and leather products are sold overseas, mostly in the form of footwear, leather garments, saddlery & harness, and finished leather.
- Export markets for leather and leather goods include the United States, Germany, Italy, France, Netherlands, Spain, Russia, Brazil, Japan, China, Singapore, and Taiwan.
2. Future of leather industry in India
An important focus area under the Make in India program is the “leather sector” because this sector is also the top ten foreign exchange earners for the country. Leather exports from India continue to thrive worldwide. A well-structured and well-established part of the Indian economy, the leather industry consists of different sectors like tanning, finishing, garments, leather goods, saddles and harnesses, etc.
- There were 36815 crores worth of leather, saddlery, harness, and leather finished products exported from India in the years 2020-21.
- Due to the increasing demand for leather products in the global markets, the export of leather and leather products from our country is expected to cross the USD 6 billion mark in the year 2022-23, according to CLE.
- Besides it, the general budget of the Indian government has provided relief to the leather industry which faces Corona and closure problems.
- In accordance with the budget, raw leather export duties have been reduced from 40% to 30% to promote exports. Additionally, the duty-free import license system, which had previously been abolished, has been reinstated.
3. Total export of leather from all over the country
- 2020-21 $3.68 billion
- 2021-22 $4.87 billion
- 2022-23 $6.00 billion (Target)
4. Total export of leather from Kanpur
- 2020-21 Rs 6500 crore
- 2021-22 Rs 9500 crore
- 2022-23 Rs 15,000 crore (Target)
5. WHY IS LEATHER MOSTLY EXPORTED FROM INDIA?
There has been rapid growth in the Indian leather industry. Indian leather exports to western countries must seem strange. Because leatherwear continues to enjoy a great deal of popularity abroad. Today, even the domestic market consumes the offerings of this industry.
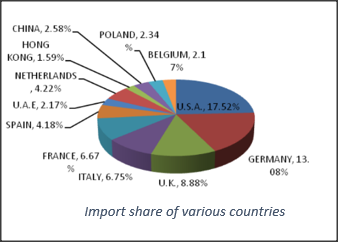
6. INDIA'S LEATHER EXPORT DATA FOR VARIOUS COUNTRIES:
- The export of leather and leather products from India crosses USD 6 billion in 2022-23: Council for Leather Exports.
-
The USA is the largest market for Indian Leather & Leather Products with 17.52 %, followed by Germany with 13.08 %, the U.K with 8.88%, Italy with 6.75%, France with 6.6the 7%, Spain with 4.18%, Netherlands with 4.22%, the U.A.E with 2.17%, China with 2.5;8%, Poland with 2.34%, Belgium with 2.17%, and Hong Kong with 2%.
- Almost 73.15 percent of India's total leather & leather product exports come from these top 12 countries mentioned above para.
- India is an exporter of 2nd in terms of leather garments, 3rd in terms of saddlery and harnesses, and 4th in terms of leather goods in the world.
7. INDIA’S LEATHER EXPORT DATA w.r.t. GOODS:
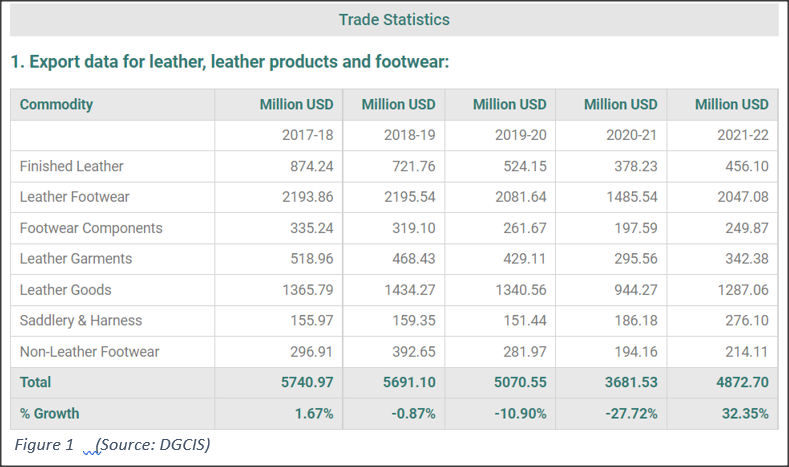
Figure 1 (Source: DGCIS)
8. STRUCTURE OF THE LEATHER INDUSTRY:
The leather industry is spread into four broad sectors, these are:
- Footwear sector
- Garments sector
- Leather goods sector including saddlery and harness
- Tanning and Finishing sector
FOOTWEAR SECTOR
It is estimated that India produces over 950 million pairs of footwear annually, making it the world's second-largest footwear producer. Export leather exports account for 28% of all leather exports, at approximately USD 400 million per year.
-
- Shoes are made from around half of the leather products worldwide: According to the International Council of Tanners (ICT), in 2015 it was around 47%.
- Depending on the model, very different types of leather are required for this - from firm leather for the sole to soft material for the upper part of the shoe, which is called upper leather. Mostly leather worldwide comes from cattle (67%), followed by sheep (12%) and pork (11%).
GARMENTS SECTOR
Indian leather is dominated by the Leather Garment Industry. Among the types of leather garments that can be classified as leather are coats, leather jackets, gloves, children's clothing, tracking jackets, and industrial garments.
- The garment industry also processed around 15% of the leather produced in 2019. Jackets, trousers, coats, and gloves are primarily made from natural material – the latter is even listed separately in the ICT statistics with a share of 4.2%.
- The garments produced are often intended to protect, for example when riding a motorbike. In addition, leather clothing, especially black, is very popular in the Sado-Maso scene. In Bavaria, lederhosen is an important part of the traditional costume.
LEATHER GOODS SECTOR
This category produces boots, belts, quivers, spectacle cases, camera gear, document cases, axe holsters, chef knife roll, mouse pads, wine dual bottle cases, etc.
Automotive industry
- With a good 17%, the automotive industry was in second place when it came to the use of leather in 201. In addition to the seats, which are usually covered with noble natural material, especially in expensive models, the cockpit is also partially covered with leather.
- Around 10% of tanned animal skins are processed in the furniture industry. Here the leather is mainly used as a hard-wearing cover for sofas and armchairs.
Sport Industry
- Although soccer balls are still often referred to as "round leather", plastic has been used for some time because it is lighter and has different flight characteristics. On the other hand, parts of various sports equipment used in gymnastics are still covered with leather, such as the rings and the horse.
INDIAN SADDLERY INDUSTRY
Saddlery and harness goods are among the most important products for export in India. Military and police equipment was the primary purpose of the saddlery industry in the 19th century when Britishers ruled over India.
TANNING AND FINISHING SECTOR
Approximately 2500 tanneries exist in the Indian market, including 1700 small-scale facilities and more than 800 manufacturing facilities. Three states are primarily involved in the tanning and finishing industry: Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu.
9. LEATHER INDUSTRY IN THE GLOBAL MARKET
- The leather industry is expanding worldwide, dealing with crust leather, finished leather, and finished leather products. There is a wide trade and use of leather and leather products around the world.
- The leather and leather goods industry is a major contributor to the world economy, generating approximately USD 180 billion in trade each year (UNIDO, 2019).
10. WHAT IS THE PROCESS OF LEATHER PRODUCTION - STEP BY STEP
Once the animal has died, the skin is removed and salt is applied to it to remove the moisture from the skin. After this, the skin is dried in the shade completely this is called cured skin and then this cured skin send to the tanneries for a further four more important processing steps and thus we obtain leather.
There are four basic processing stages in the production of all types of leather:
- Stages of preparation
- A tanning session
- Re-tanning
- The last step i.e. finishing
1. Preparatory steps: In the preparatory steps we perform various processes and in each process, we remove unwanted raw skin components.
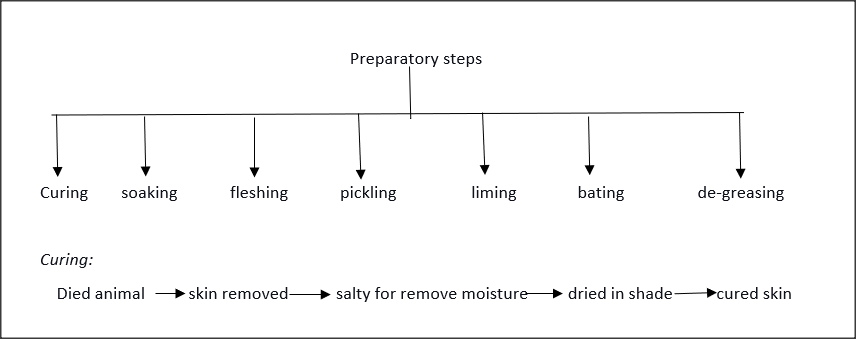
Soaking:
During this process, the skins are immersed in water for a few days to restore the moisture lost during the salting process, as well as to remove dirt, blood, debris, etc.
Fleshing:
In this process, we remove the flesh under the skin with the help of machines. After this process or after tanning, we can split the hide into different layers i.e. full grain, top grain, corrected grain, etc.
Pickling:
As part of this process, we use chemical acids like chromium and aldehydes to prevent the hide from decomposition.
De-pickling:
As a result of pickling, the pH level of the skin increases dramatically. To reduce the pH level, the skin is dipped in sulphuric acid. This is called de-pickling.
Liming:
A solution of water with sodium sulfide and hydrate is applied to the skin to remove the hair and wool. But the absorption of water by the skin results in swollen skin.
De-liming:
De-liming is a process in which water is mixed with ammonium chloride or ammonium sulfate to wash the skin. In this way, the water is removed (which was absorbed by the liming process) and the swelling of the skin is reduced.
Bating:
Proteolytic bating enzymes are used on the skin to remove non-fibrous proteins. It cleans the grain and makes the skin smooth and soft.
De-greasing:
Water-based solutions are used to remove excess grease (natural fatty acid) from the skin.
2. Tanning session:
Tanning is the process in which the protein of the rawhide is converted into durable material i.e. non-decomposable and sturdy material. The most common tanning which is used in the tanneries are:
- Vegetable tanning
- Chrome or mineral tanning
- Aldehyde tanning
- Oil tanning
Vegetable tanning:
It does not mean that vegetables are used in vegetable tanning; it means the active ingredients in vegetable tanning are found in bark, leaves, oak trees, mimosas, and the like. The vegetable tanning process is time-consuming and expensive. It takes about 30 days to complete the process. However, it does not harm the environment, and this process produces highly durable leather.
Chrome or mineral tanning:
Chrome tanning is very popular because of its process including its quickness, inexpensiveness, and simplicity. Before this process began in 1857, only vegetable tanning was available. This process takes at most 24 hours to complete the process. In this process, the chromium (3) sulfate molecule is used as a tanning agent. The size of the chromium molecule is less than the vegetable molecule. Therefore, the leather made from chrome tanning is thinner and softer than vegetable tanning. Chrome-tanned leather is also called wet blue leather because of its blue color. But this tanning method is not healthy for the environment.
Aldehyde tanning:
It is chrome-free leather. The agent used in aldehyde tanning is glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine. It is also called "wet-white" leather.
Oil tanning:
A method of tanning in which dry hide by adding oil and fat to it until it replaces its natural moisture is known as oil tanning.
3. Re-tanning:
Re-tanning is the process in which we produce products for the market. We decide the color and texture of the product during the re-tanning process. There are several stages including in re-tanning:
- Drying
- Shaving
- Splitting
- Dyeing
- Fat liquoring/stuffing
Drying:
In this process, water is removed from the tanned leather with the help of a rolling machine.
Shaving:
The leather is made uniformly thick with this method by removing the meat residue with the help of a rolling machine.
Splitting:
Using a split machine, we can split thick leather into several layers even after liming. Because grain is present in the top layer of leather, it is the most expensive. Leather without grain is called suede. Suede leather is sometimes sold at high prices with artificial grains.
Dyeing:
The upper surface of all types of leather except vegetable-tanned leather has been dyed.
Fat liquoring/stuffing:
The fat, oil, and wax are filled between the fibers of the leather to keep it soft and flexible, otherwise, the leather will become dry and hard.
4. Finishing:
As a final step, we determine what color, thickness, and texture the final product should have. It involves:
- Polishing
- Embossing
- Surface coating
Polishing:
To enhance the leather's shine, it has been polished
Embossing:
It is done by a 3D printer using hydraulic rollers.
Surface coating:
In dry finishing, the leather is given its final appearance with the help of various mechanical and chemical treatments. Here it is decided whether the leather should have a shiny or matt and a smooth or grained surface. By printing or embossing the leather, the look can be changed significantly and adapted to current fashions or customer preferences.
Final inspection:
Before the leather is dispatched and begins its journey to the leather goods factory, it goes through one last check. This ensures that all requirements were met during production. The leather is then sorted, measured, packaged, and shipped according to its quality characteristics.
If you want to learn how to procure leather or if you want to visit the leather industry, you can join us. We can help you with the practical field visit for leather products export business knowledge. So come and join live with us. We are procurement/ sourcing agents of Leather products for exports. Feel free to contact us at any time. We are available 24/7. We have vast experience in this field. We have several experts who will guide and assist you at each step of your business.
11. DIFFERENT TYPES OF LEATHER ARE EXPLAINED IN DETAIL:
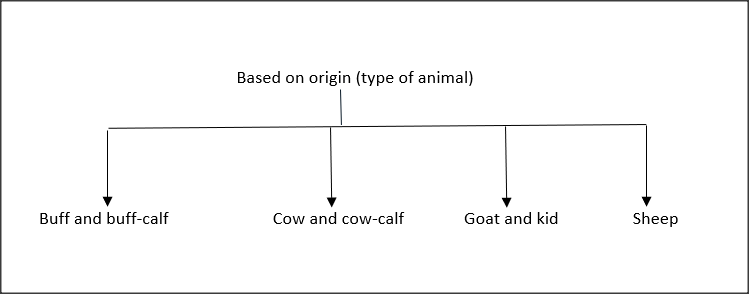
In addition to the animal origin (type of animal), grain appearance, tanning, and finishing, leather also be classified into different categories:
- Based on origin ( type of animal )
- Based on grain structure
- Based on finishing
Leather is made from skins and hides which are gathered from meat factories. A large animal's outer covering is called hide, while a small animal's outer covering is called skin.
- The rawhide/skin (H/S) is first converted into wet blue (After the tanning operation the raw H/S is called wet blue.), and then wet blue is converted into finished leather.
The following diagram helps explain this:
Raw H/S > wet blue > crust > finished leather
- In terms of uppers (upper part of the shoe), leather is suitable material since it has strength, durability, long-lastingness, and flexibility.
LEATHER-BASED ON ORIGIN:
LEATHER-BASED ON GRAIN STRUCTURE:
Second, leather can be classified by the appearance of its grain pattern, i.e. whether it was originally patterned, if it was artificially patterned, or if a special effect was applied, e.g. velvety texture.
Leather-based on grain structure
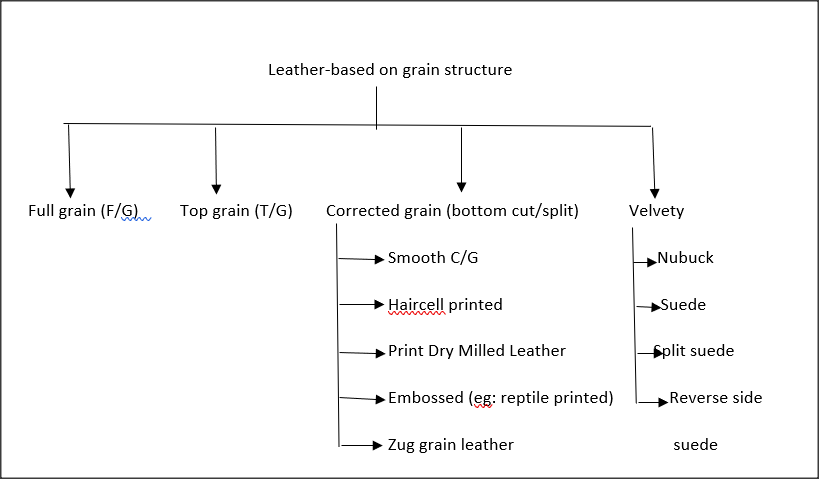

FULL GRAIN LEATHER (F/G):
Full grain refers to F/G. The original grain pattern can be seen on this leather. The rawhide/skin from which this leather is derived is almost defect-free since the finishing does not cover the grain. Therefore, F/G leather is expensive. This looks natural. The finish is usually aniline or semi-aniline on this type of leather. Sometimes, we can find F/G leather with a pigmented finish then it is called pigmented leather.
TOP GRAIN LEATHER (T/G):
In terms of leather quality, the top grain is the second highest. Splitting the top layer of hiding from blemished hides produces top-grain leather. A sanding process is used to remove any inherent imperfections from the surface. The leather's appearance is enhanced by pigmentation or staining is on it.
CORRECTED GRAIN (BOTTOM CUT / SPLIT) LEATHER (C/G):
The leather is buffed from the grain side of the raw H/S is defective and then finished, plated, and given a pigmented finish once again. This leather is called corrected grain leather, often denoted by C/G, because the grain pattern is corrected throughout the whole process to hide defects and increase cutting value. Various names are used to describe C/G leather-based on its designs and plates, such as smooth C/G leather, hair cell-printed leather, Rambler leather, Zug grain leather, booty leather, etc.
VELVETY LEATHER:
Under this category, you will find nubuck, suede, split suede, and reverse side suede. A velvety appearance can be achieved by snuffing (with a fine emery paper) and buffing (rubbing with a coarse emery paper) the leather on either the grain side or the flesh side. During this process, small fibers called naps are raised on the surface, giving the material a velvety appearance.
Nubuck
During the snuffing process, the grain side of nubuck leather is made velvety. The writing effect on this leather is excellent. The writing effect occurs when raised naps are present on the surface. We get finger marks on these leathers when we touch them with our fingers. This effect is called the writing effect.
Note: Buff nubuck has a low writing effect.
Suede
If the grain side is having more deep defects it is made velvety by buffing the grain side. This leather is called suede.
Split suede
It is called split suede if the leather is velvety on both sides. Course fibers of a similar look are visible from both sides. You can use this leather on both sides.
Reverse Side Suede
In the case of completely defective grain sides, the fresh side is made usable by giving it a velvety appearance. This type of leather with a reverse side is known as reverse side suede.
LEATHER-BASED ON FINISH:
Finishing leather
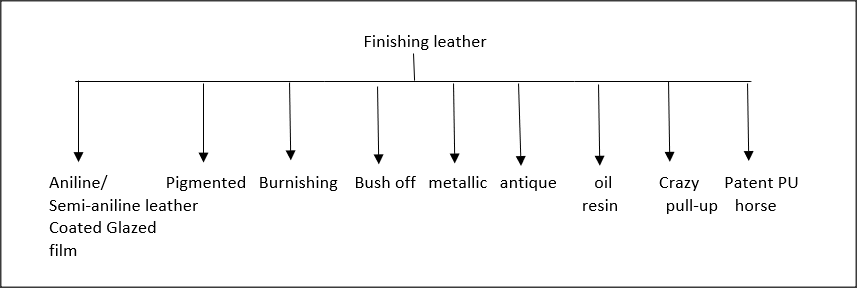
These are the common finishes available in the leather used for upper making:
- Aniline or semi-aniline leather: An aniline or semi-aniline finish gives the leather a luxurious and transparent look. There are often shade variations in this type of leather. Grain matching and shade matching are essential when cutting aniline or semi-aniline leather. A glazed finish is a natural finish commonly found on goat/baby leather. It has a very beautiful, natural glow to it.
- Pigmented: This type of leather finish is usually applied to the grain of the leather to hide blemishes or imperfections. A heavy coat of pigmented finish, which gives a very nice covering effect, is applied to the leather.
- Burnish: This type of finish can be given by a wax called burning wax, which generates a shine or burning gloss on super abrasive action (by rubbing the surface). This finish is typically offered on F/G type of leather.
- Brush off leather: Brush off leather is the leather in which we give a two-tone effect with a heavy cotton brush. Leather is finished by coating two or three times in a tannery. The two finish layers are either in contrast colour or contrast shade. The top coat is not fixed and on brushing hard gets off. Hence, the name given to the finish is Brush off. You brush the surface and the top finish is off making the bottom finish layer visible giving the leather a two-tone effect. This leather is called brush off.
- Metallic: The leather is given a metallic finish to make it look like metal. The metallic colour is added to leather while it is prepared, used for ladies' kid’s shoes.
- Antique: A type of leather treated to look rugged or vintage. Often, the top coat of leather gets rubbed off unevenly, revealing a pale underlying color underneath. This finish has a weathered appearance or cloudy effect. When shopping for leather furniture and accessories, shoppers are often drawn to this weathered look.
- Oil pull-up: This leather is oily in nature. By pulling or folding the leather, you remove the oil that has been deposited between the layers. Hence, this finish also gives a two-tone effect to the leather. Normally, this effect is applied to F/G leather. Even milled leather sometimes has an oil pull-up effect. This leather is called a milled oil pull-up.
- Crazy horse: During the process of making Crazy Horse Leather, we apply a thick, smooth coating of wax on full-grain leather. This leather has a utilized look with a low pull-up effect.
- Patent PU Coated or PU Film Coated: Patented leather is split leather with a thick layer of polyurethane (PU) laminated on top. This leather does not break like leather because of the thick PU film. There are various types of PU film-coated leather. It can either be split or sometimes F/G leather coated with a very thin film of PU. This leather breathes.
12. Important abbreviations for different types of leather
Abbreviations from the English-speaking world are often used in the fashion industry to describe the different types of leather:
- DDDM (Drum dyed, dry milled leather): drum dyed, dry milled
- DDDN (Drum dyed, dry Napa): barrel-dyed, dry napa
- NDM (Natural dry milled leather): dry milled
- PDM (Printed dry milled leather): embossed, dry milled
13. Recognizing leather types: tips
Tip 1: Pigmented smooth leather feels both fine and coarsely structured.
Tip 2: Thanks to the protective layer of color, the pores of smooth leather absorb much less moisture.
Tip 3: If you get this type of leather wet, it will hardly look darker.
Tip 4: The pores of aniline leather are open, allowing moisture to penetrate deeper. A dark spot will become visible if you put some water on the surface.
Tip 5: As soon as you stroke nubuck, suede, or suede leather, the material casts shadows.
14. Important Tips before sourcing leather as well as leather products for export
- Aim for the flexibility and adaptability of leather.
- Always rely on experienced suppliers.
- We strive for long cooperation with our clients.
- Be good at communication as continuous price negotiations may take place with your suppliers according to optimizing always our prices.
- Always ensure that you are getting what you ordered. Confirm that the quality of the goods differs from the sample.
- The leather supplier should hold a large stock of leather scraps from well-known upholstery manufacturers and car seat manufacturers. The leather supplier should offer several hides and half-hides in different colors and qualities.
- The leather supplier should offer the most of articles over an extended period. What this means for you: You can better plan your production.
- The leather and leather scraps should be stored properly in our warehouse (dry, at the right temperature, and not exposed to direct sunlight), so there is no loss in quality.
- Select the suppliers with care to offer you the best possible quality at a reasonable price.
- You decide if you would like to collect the goods yourself or if you would like us to arrange the delivery for you.
15. LIST OF LEATHER PRODUCTS:
Body items
Garments, Jackets, Shoes, Belt, Bracelets, Hats, Boots, Gloves, Sandals, Watch straps, Bike gloves, etc.
Container and holders
Purses, key holders, mobile phone holders, spectacle cases, laptop cases, air-pod cases, wallets, card holders, billfolds, journals, cup coasters, mouse pads, pen covers, camera gear, passport covers, shaving cases, document cases, wine bottle case, axe holster, chef knife roll, etc.
Defence and Protective items
Knife sheaths, Holsters, Belts, Quivers, Harness, Straps for firearms, etc.
Home & Office items
Sofas, Footrest, Chair backs, Armrests, Leather wall hanging, Mats, Carpets, Etc
Decor items
Bible cover, photo album, leather family milestone tree, etc.
Jewelry
Vestige, Cuffs, Ornaments, etc.
Luggage
Duffels, Makeup bags, Shaving bags, Totes, etc.
Music and entertainment items
Drums, Instrument straps, Musical instrument bags/holders, Guitar straps, Harmonica leather case, etc.
Dog Accessories
Collars, Chains, Gags, Muzzles, Harness, Saddles, leashes, etc.
Horse accessories
Horse brow-bands, chaps + breeches, reins, horse leads, bridle with and without padding, saddle (English, western, Portuguese), horse riding belt, headstall with breastplate, etc.
Religious & magical items
Drums, skins, praying mats, prayer alters, scepters, amulets, talismans, flying whisks, etc.
Sports items
Footwalls, baseball gloves, cricket gloves, soccer gloves, etc.
Travel items
Steering wheel cover, neck pillow, headrests, double-tray Dopp kit, etc.
Upholstery
Airplane seat, cinema hall seat, sofa seat, car seat, auditorium seat, etc.
16. HOW TO START YOUR LEATHER BUSINESS – STEP BY STEP
STEP 1 Plan your Leather Business
- Ascertain your start-up and ongoing costs
- Select your target market
- How much can you charge customers?
- Select a name for your company
STEP 2 Watch Barai Overseas Day 1 to 20 Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YyiHQjx7O4E&list=PL-N8-2Kxv68afhyxPnHlaH9qKBoDyFFQV
STEP 3 Open a Business Bank Account & Credit Card for E-Commerce
You will surely need a bank account for transactions and other matters.
STEP 4 Approach CHA and Plan Shipping and Logistics, Must complete your port registration formalities
The organized procedure with product record keeping is also necessary.
STEP 5 Get the essential documents and licenses for the Leather Business
You also need to obtain essential documents and licenses for the Leather Business
You may visit https://leatherindia.org/
STEP 6 Get Fiverr Gigs Support for your Support
You may visit Fiverr or take expert help to find the best gigs for logos, websites, brochures, and all. You may visit https://www.baraioverseas.com/store.html
STEP 7 Create your Leather Business Website
As everything is going online nowadays so you need to set up and promote a website regarding your leather products.
STEP 8 Hire Sourcing Agent for Practical Knowledge of Products
Blog Credits: https://www.fiverr.com/ajeetsingh430
Tags: Leather Export Business Made Easy